
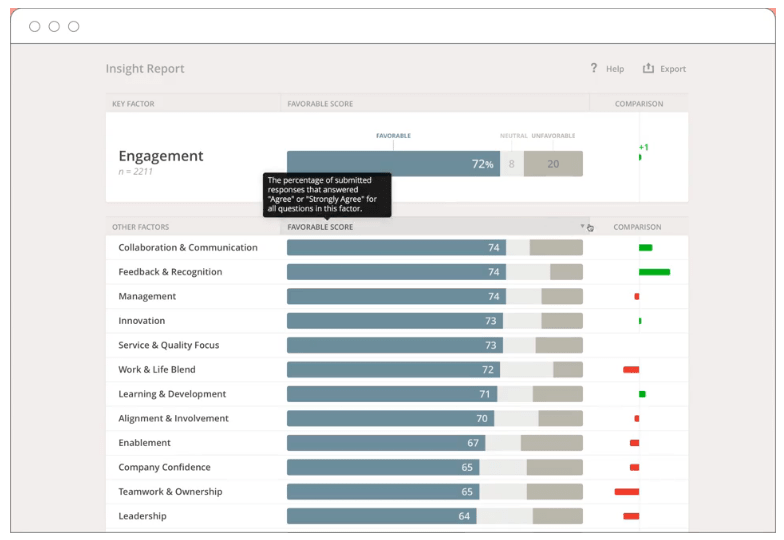

You have the ability to customize your reporting and analysis and focus on employee groups filtered by a manager, project group, tenure, and more. Their reporting is different than traditional broad turnover metrics and formulas.
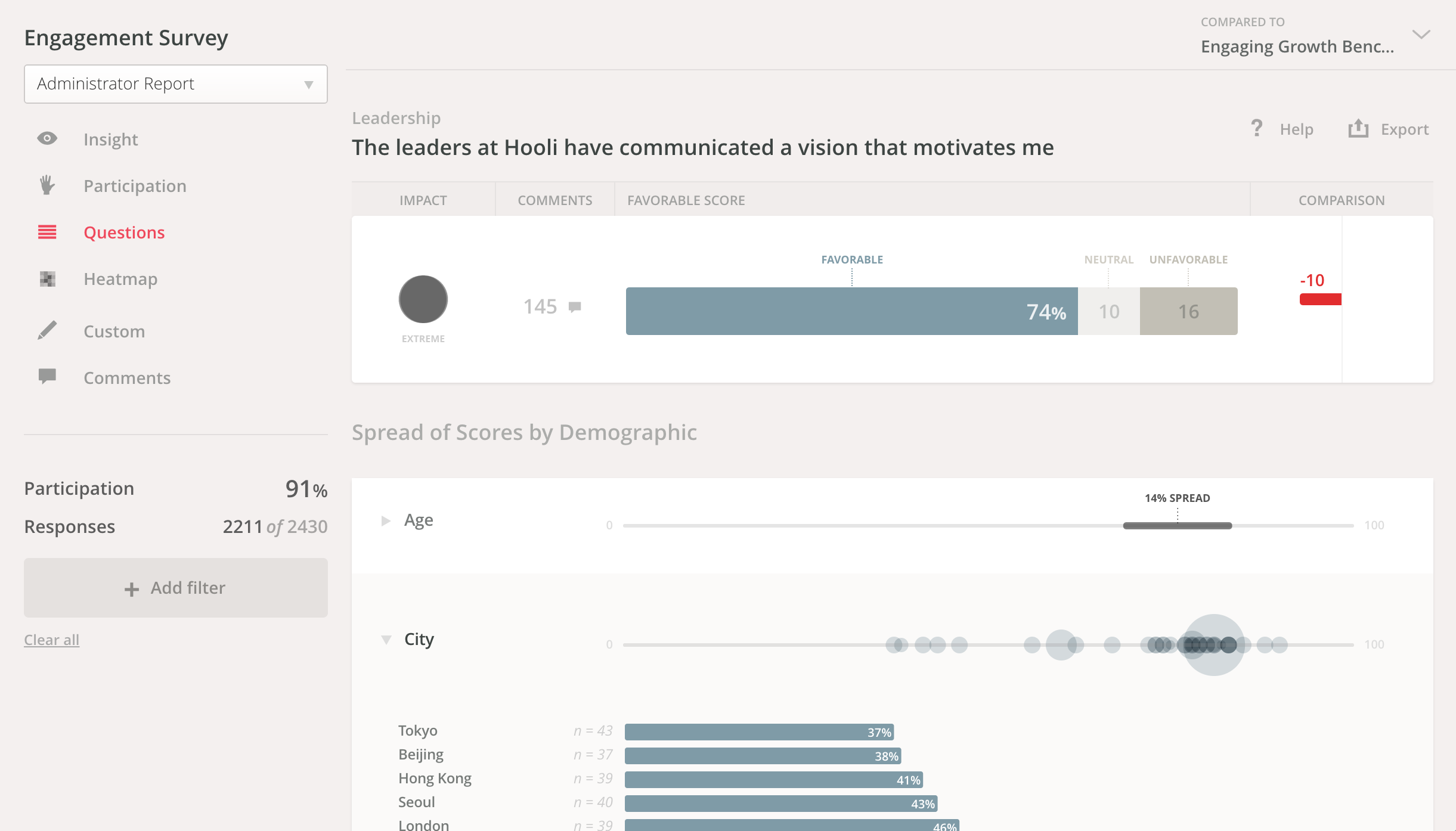
One of my favorite features in Culture Amp’s platform is turnover analysis. Driving Awareness and Education on Turnover Trends and Manager Impact
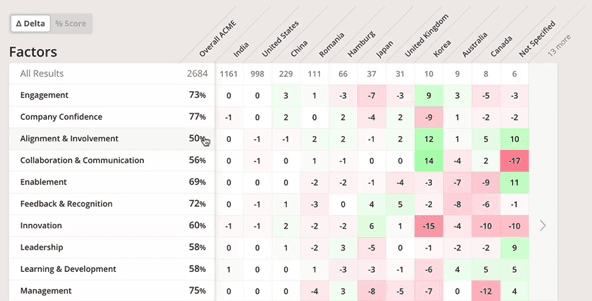
The Culture Amp platform is different, it offers ongoing intuitive checks and balances for employees at all levels within an organization. Traditional engagement surveys provide a snapshot in time, measuring levels much like a dam. Engagement levels can ebb and flow even multiple times a week. They are a company that drinks their own champagne and are committed to creating a technology platform that goes beyond traditional employee surveys- They give managers and HR leaders up to the second insight into their employee engagement levels and trends.Īs I mentioned, employee engagement is never static. Having been present on thousands of demos over the last 10 years, I continue to be incredibly impressed with Culture Amp. To add some context, it’s worth noting that G2 article states, 66% of HR employees believe that employee engagement has increased over the past year, yet only 34% of non-HR employees feel more engaged over the same time period.Įarlier this month, I had the pleasure of seeing a demo of the People and Culture platform, Culture Amp. One of the greatest workplace mysteries is employee engagement: it’s challenging to understand what drives performance, satisfaction, and happiness at work. See our FTC disclosure at the end of this review. The progression through the G2/M checkpoint is mediated again by increased cAMP levels.Learn more about our HR Technology and Product Reviews here at Workology. Since cAMP retains cells in the G1 phase, cytokines of the TNF-alpha group are required for cell proliferation inducing the entry into the S phase. The increase of cAMP levels activates the conversion of lipocytes into myofibroblasts and increases the number of cells that can participate in repair. Our results suggest that inflammation-dependent activation of stellate cells occurs in ordered interaction and coordination of proinflammatory agents. Actin cytoskeleton reorganization was observed after 24 h treatment, indicating increased cell motility. This effect was abrogated by dibutiryl-cAMP. SCS and TNF-alpha diminished the culture cell density, with an increase of cell thymidine incorporation and of cellular protein content, indicating an arrest in the G2/M phase of the cell cycle, which was reversible 48 h after removal of SCS. The present study investigated the effects of SCS and TNF-alpha on the GRX cell proliferation and on the organization of the actin cytoskeleton. We have recently shown that they respond to inflammatory mediators and cytokines present in the concanavalin A-activated spleen cell supernatant (SCS) by quantitative changes in the expression of intermediate filaments. GRX cells are a model of hepatic stellate cells characterized as myofibroblasts by morphological and biochemical criteria. Hepatic fibrosis is a common response to chronic liver injury and is characterized by increased production of extracellular matrix components, whose major part is produced by hepatic stellate cells activated by inflammatory mediators to proliferate and migrate into the injured regions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
